Blockchain 101: Aloha to a New Digital Frontier
Welcome, fellow financial, crypto and fintech enthusiast! In this post, we’re diving into the fascinating world of blockchain—a technology that’s transforming industries around the globe. Whether you’re a curious local, an entrepreneur, or simply eager to learn about emerging digital trends, this guide will break down blockchain in simple terms.
What Is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. Imagine a digital notebook that isn’t stored in one single place but is shared across a network of computers. Every time a new record (or “block”) is added, it links to the previous one, creating a secure and unchangeable “chain” of data. This decentralized system means that no single person or entity has complete control, which enhances transparency and security.
Key Features:
- Decentralization: No central authority manages the ledger.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered.
- Transparency: All participants can view the transactions.
How Does Blockchain Work?
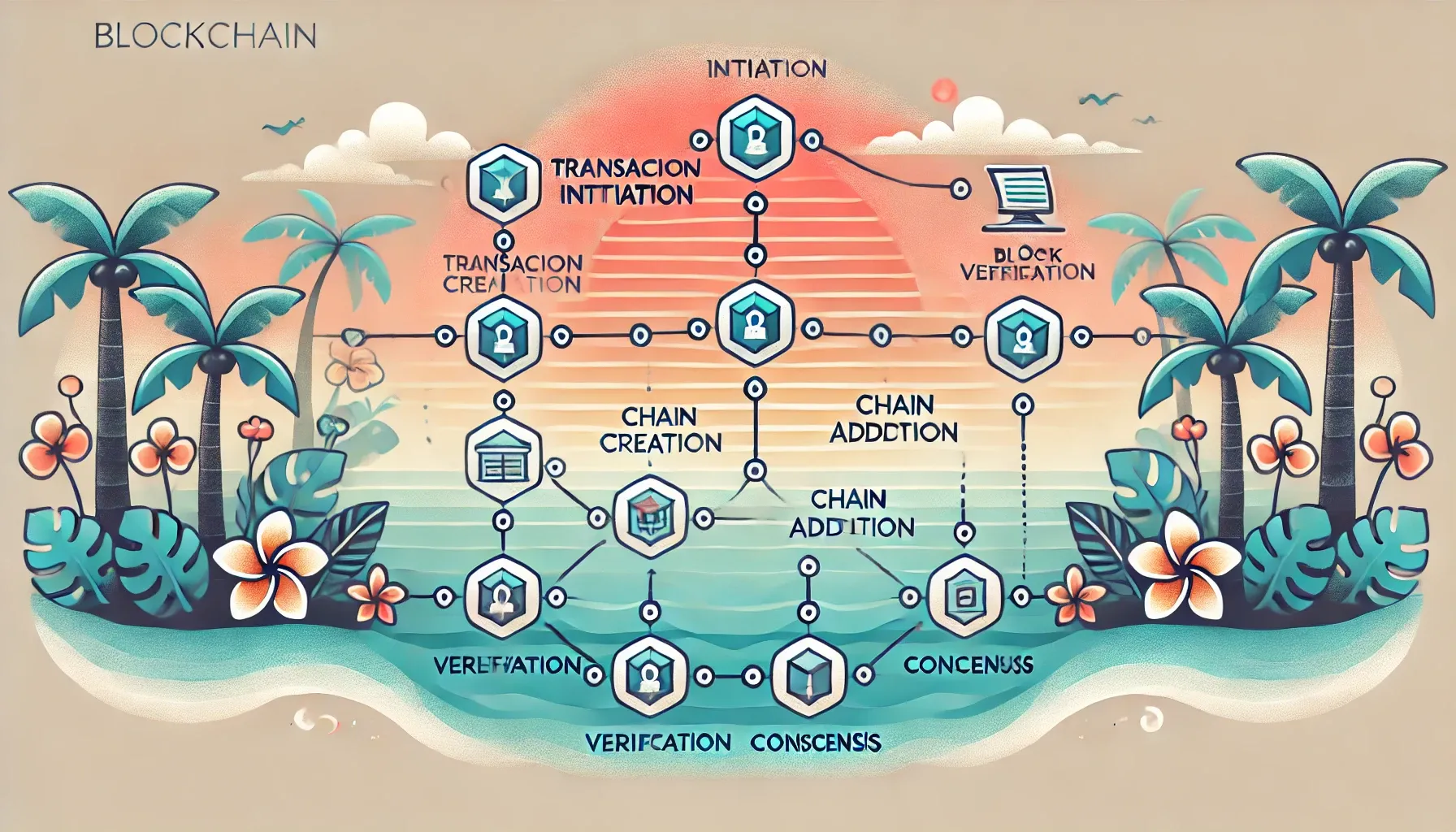
Blockchain operates through a series of steps:
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction (for example, sending cryptocurrency or recording data).
- Block Creation: The transaction is grouped with others into a block.
- Verification: Multiple nodes (computers) in the network verify the block’s authenticity using complex algorithms.
- Chain Addition: Once verified, the block is added to the existing chain in a linear, chronological order.
- Consensus: The network reaches consensus, ensuring that every participant has the same updated ledger.
This process ensures trust and integrity without needing a central authority, making it ideal for applications like digital currencies, smart contracts, and secure data sharing.
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain
Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Data is cryptographically secured, making it extremely difficult to tamper with.
- Increased Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants, fostering trust.
- Decentralized Control: Eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and potential points of failure.
Challenges:
- Scalability: As the number of transactions increases, so does the computational load on the network.
- Energy Consumption: Some blockchain networks (especially those using proof-of-work) require significant energy, which is a concern even in resource-rich areas like Hawaii.
- Regulation: The emerging nature of blockchain often outpaces regulatory frameworks, creating uncertainty for businesses and consumers alike.
Blockchain and the Aloha Spirit: What It Means for Hawaii
Blockchain isn’t just about cryptocurrencies—it has the potential to revolutionize how we conduct business and manage information locally. Imagine:
- Secure Land Title Registries: Enhancing transparency and reducing fraud in property transactions.
- Local Supply Chains: Ensuring that local produce and products are tracked from farm to table.
- Community Engagement: Empowering local governments and organizations with more transparent systems for voting and civic participation.
By integrating blockchain technology, Hawaii can lead the way in creating innovative, secure, and efficient digital ecosystems that honor our unique cultural heritage and natural resources.
Conclusion
Blockchain is more than just a buzzword—it’s a transformative technology that offers security, transparency, and innovation. As Hawaiians, embracing this technology could pave the way for new opportunities in business, governance, and everyday life. Whether it’s enhancing local supply chains or securing digital transactions, the potential for positive change is immense.
Mahalo for reading, and stay tuned for more insights into the digital future!
References: